Brainpop 3 branches of government – BrainPOP’s Three Branches of Government offers a comprehensive and engaging exploration of the intricate system of checks and balances that defines the American government. Through a combination of engaging videos, interactive quizzes, and detailed explanations, BrainPOP provides a comprehensive understanding of the roles and responsibilities of each branch and how they work together to ensure a balanced and effective government.
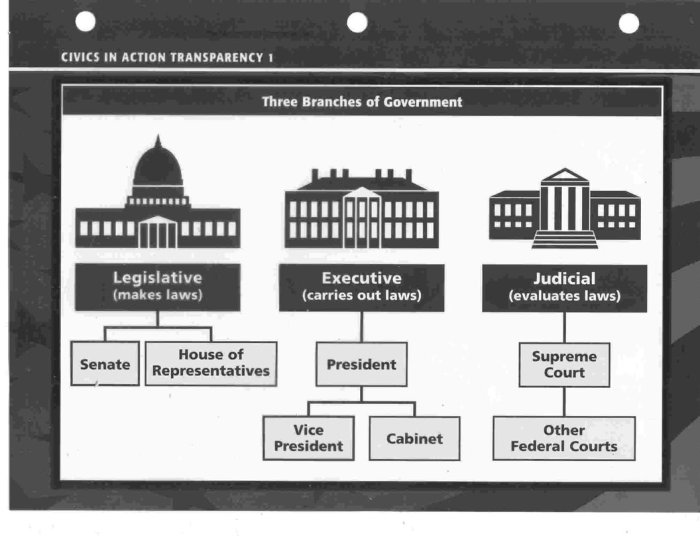
Beginning with a brief overview of the three branches – legislative, executive, and judicial – BrainPOP delves into the specific functions and powers of each branch. The legislative branch, consisting of the House of Representatives and the Senate, is responsible for making laws, while the executive branch, led by the President, is responsible for enforcing laws and managing the day-to-day operations of the government.
The judicial branch, represented by the Supreme Court, is responsible for interpreting laws and ensuring their constitutionality.
Introduction to BrainPOP’s Three Branches of Government: Brainpop 3 Branches Of Government

BrainPOP is an educational website that uses animated videos, games, and other interactive activities to teach students about various subjects. One of its most popular units is on the three branches of government. This unit provides a comprehensive overview of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches of the United States government, and how they work together to create a system of checks and balances.The
three branches of government are:*
-*Legislative Branch
The legislative branch is responsible for making laws. It is made up of the Senate and the House of Representatives.
-
-*Executive Branch
The executive branch is responsible for carrying out laws. It is headed by the President of the United States.
-*Judicial Branch
The judicial branch is responsible for interpreting laws. It is made up of the Supreme Court and other federal courts.
Legislative Branch
The legislative branch is responsible for making laws. It is made up of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Senate has 100 members, two from each state. The House of Representatives has 435 members, who are elected from districts based on population.The
legislative process begins when a bill is introduced in either the Senate or the House of Representatives. A bill is a proposed law. Once a bill is introduced, it is assigned to a committee for review. The committee can hold hearings on the bill and make changes to it.
If the committee approves the bill, it is sent to the full Senate or House of Representatives for a vote.If the bill passes both the Senate and the House of Representatives, it is sent to the President for his signature.
The President can sign the bill into law, or he can veto it. If the President vetoes the bill, it can be overridden by a two-thirds vote of both the Senate and the House of Representatives.
Executive Branch, Brainpop 3 branches of government
The executive branch is responsible for carrying out laws. It is headed by the President of the United States. The President is also the commander-in-chief of the armed forces.The President has a number of powers, including the power to veto laws, appoint judges, and grant pardons.
The President also has the power to make treaties with other countries.The President is assisted by a number of departments and agencies, including the State Department, the Department of Defense, and the Department of Justice. These departments and agencies help the President to carry out his duties.
Judicial Branch
The judicial branch is responsible for interpreting laws. It is made up of the Supreme Court and other federal courts. The Supreme Court is the highest court in the United States. It has the power to review laws and decisions made by lower courts.The
Supreme Court has a number of powers, including the power to declare laws unconstitutional. The Supreme Court also has the power to interpret the Constitution.The Supreme Court is made up of nine justices. The justices are appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate.
The justices serve for life.
Checks and Balances
The three branches of government are designed to work together in a system of checks and balances. This system prevents any one branch from becoming too powerful.For example, the legislative branch can make laws, but the executive branch can veto them.
The judicial branch can interpret laws, but the legislative branch can override those interpretations. The executive branch can appoint judges, but the judicial branch can review those appointments.The system of checks and balances ensures that no one branch of government can become too powerful.
It also ensures that the government is responsive to the needs of the people.
Quick FAQs
What is the purpose of checks and balances?
Checks and balances are designed to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful. Each branch has the ability to check the power of the others, ensuring that no single branch can dominate the government.
How does the legislative branch check the power of the executive branch?
The legislative branch can check the power of the executive branch by passing laws that limit the President’s authority, by conducting investigations into the executive branch, and by impeaching the President.
How does the judicial branch check the power of the legislative branch?
The judicial branch can check the power of the legislative branch by declaring laws unconstitutional. The Supreme Court has the power to review laws passed by Congress and determine whether they violate the Constitution.