Cellular respiration an overview pogil – Cellular respiration, an overview POGIL, delves into the intricate processes that sustain life, providing a comprehensive exploration of the mechanisms by which cells generate energy.
Cellular respiration encompasses a series of biochemical reactions that convert nutrients into energy, primarily in the form of ATP. This process plays a pivotal role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, supporting growth, and facilitating various cellular functions.
Cellular Respiration Overview
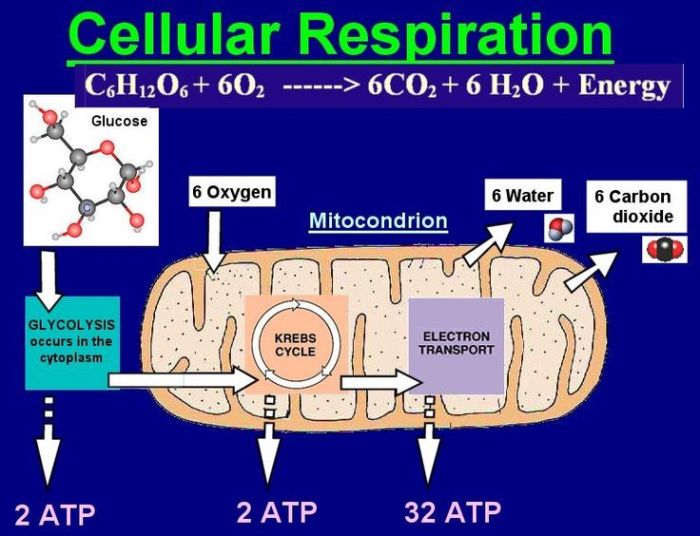
Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic reactions that convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells. This process occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells.
Stages of Cellular Respiration, Cellular respiration an overview pogil
- Glycolysis: Occurs in the cytoplasm and breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate, producing ATP and NADH.
- Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): Takes place in the mitochondrial matrix and further breaks down pyruvate, generating ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
- Electron Transport Chain: Located in the inner mitochondrial membrane, it uses the energy from NADH and FADH2 to generate ATP through oxidative phosphorylation.
Importance of Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration provides the energy necessary for various cellular processes, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and protein synthesis. It also generates intermediate molecules used in biosynthesis and other metabolic pathways.
Glycolysis
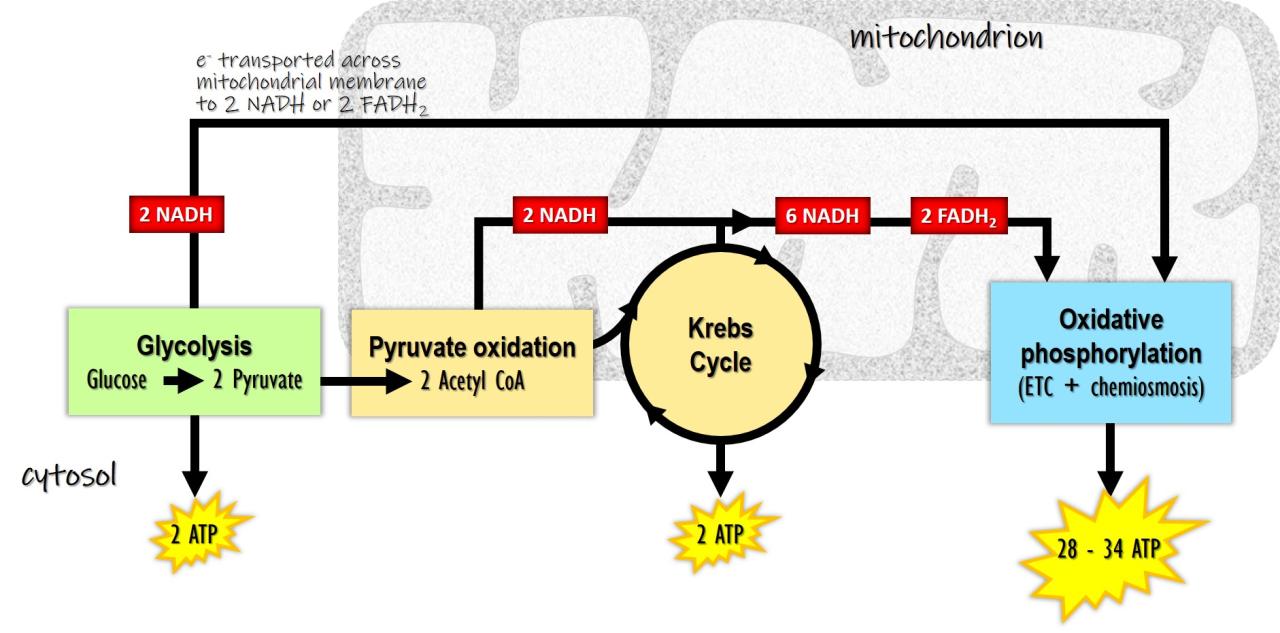
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration, occurring in the cytoplasm. It involves the breakdown of glucose, a six-carbon sugar, into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon molecule.
- Steps of Glycolysis:Consists of 10 enzymatic reactions, including phosphorylation, isomerization, cleavage, and oxidation.
- ATP and NADH Production:Generates 2 molecules of ATP and 2 molecules of NADH per molecule of glucose.
- Preparation for Krebs Cycle:Converts glucose into pyruvate, which serves as the starting molecule for the Krebs cycle.
Krebs Cycle: Cellular Respiration An Overview Pogil
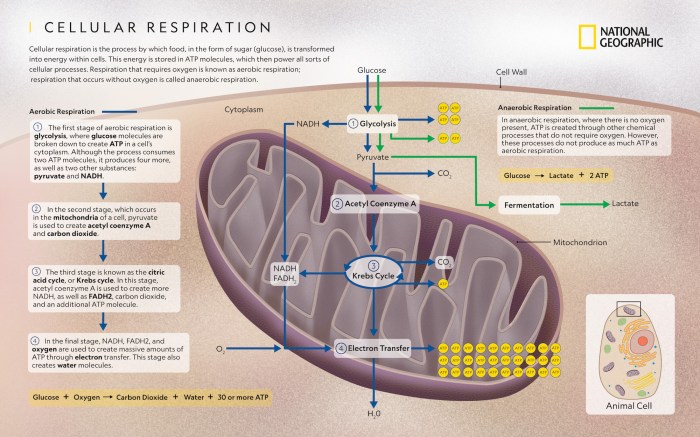
The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, takes place in the mitochondrial matrix. It further breaks down pyruvate from glycolysis, releasing energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
- Steps of the Krebs Cycle:Involves a series of enzymatic reactions, including condensation, oxidation, and decarboxylation.
- ATP, NADH, and FADH2 Production:Generates 2 molecules of ATP, 3 molecules of NADH, and 1 molecule of FADH2 per molecule of pyruvate.
- Energy Generation:Releases large amounts of energy, providing the majority of ATP produced during cellular respiration.
Electron Transport Chain
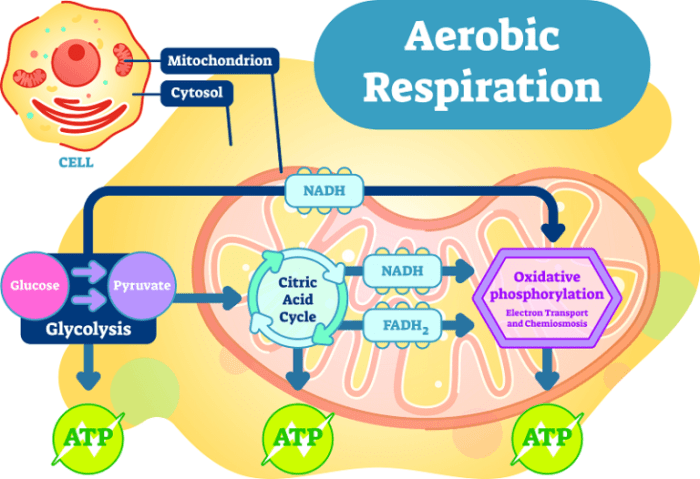
The electron transport chain is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It uses the energy from NADH and FADH2 to generate ATP through a process called oxidative phosphorylation.
- Structure and Function:Consists of a series of protein complexes that transfer electrons along a gradient.
- ATP Generation:The electron flow drives protons across the membrane, creating a gradient that is used to synthesize ATP.
- Oxidative Phosphorylation:The final stage of cellular respiration, where most of the ATP is produced.
Top FAQs
What is the primary function of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration’s primary function is to generate energy in the form of ATP, which serves as the primary energy currency for cells.
What are the key stages of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration consists of three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle), and the electron transport chain (oxidative phosphorylation).
How does cellular respiration contribute to the production of food and beverages?
Cellular respiration is essential in various industrial processes, including the production of food and beverages. For example, it is involved in the fermentation of sugars to produce alcoholic beverages and the generation of ATP during the baking process.