Interactive tutorial fluids and electrolytes – Interactive Tutorial on Fluids and Electrolytes: A Comprehensive Guide. This interactive tutorial provides an in-depth exploration of fluids and electrolytes, their functions, and their clinical significance. Through engaging exercises, simulations, and case studies, learners will gain a thorough understanding of fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalances, and management strategies.
Fluids and electrolytes are essential components of the human body, playing a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis. This tutorial will delve into the intricate world of fluids and electrolytes, providing a comprehensive overview of their properties, functions, and clinical implications.
Interactive Tutorial Overview
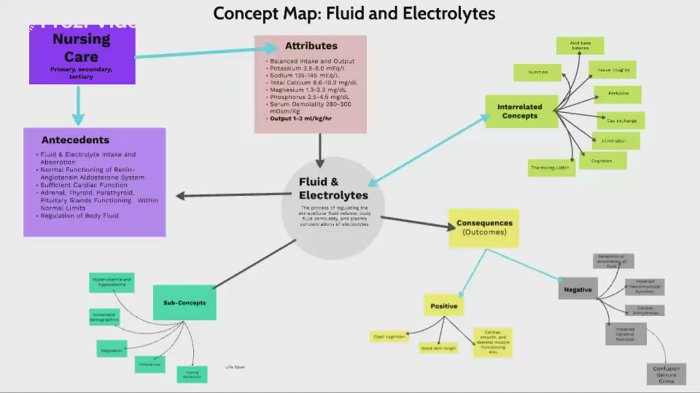
Interactive tutorials provide an engaging and effective way to learn about fluids and electrolytes. They allow learners to interact with the material, apply their knowledge, and receive immediate feedback. Interactive tutorials can include simulations, case studies, quizzes, and other activities that enhance the learning experience.
Interactive tutorials offer several benefits and advantages, including:
- Increased engagement and motivation
- Improved knowledge retention
- Enhanced critical thinking skills
- Real-time feedback and reinforcement
- Personalized learning experience
Examples of interactive tutorials that effectively teach about fluids and electrolytes include:
- Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Tutorial by the University of Utah
- Interactive Fluid and Electrolyte Tutorial by the American Association for Clinical Chemistry
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Simulation by the National League for Nursing
Essential Fluid and Electrolyte Concepts

Fluids and electrolytes are essential for maintaining homeostasis in the body. Fluids make up about 60% of body weight and are distributed between intracellular and extracellular compartments. Electrolytes are minerals that are dissolved in fluids and play a vital role in various physiological processes, such as maintaining blood pressure, regulating nerve function, and facilitating muscle contraction.
Maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance is crucial for optimal health. Imbalances can occur due to various factors, such as dehydration, excessive fluid loss, or electrolyte disturbances. These imbalances can lead to serious health consequences, including dehydration, hyponatremia, and hyperkalemia.
The different types of fluids and electrolytes in the body include:
- Intracellular fluid (ICF):Fluid inside the cells, containing potassium, magnesium, and phosphate
- Extracellular fluid (ECF):Fluid outside the cells, including plasma (blood) and interstitial fluid (fluid between cells), containing sodium, chloride, and bicarbonate
- Electrolytes:Sodium, potassium, chloride, bicarbonate, calcium, magnesium, and phosphate
Assessment of Fluid and Electrolyte Status
Assessing fluid and electrolyte status is essential for detecting and managing imbalances. Various methods are used, including:
- Physical exam:Assessing skin turgor, mucous membranes, and capillary refill time can provide clues about hydration status.
- Laboratory tests:Blood tests, such as serum electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and creatinine, can provide information about electrolyte levels and kidney function.
- Urine tests:Urine specific gravity and osmolality can indicate hydration status and electrolyte excretion.
- Monitoring vital signs:Heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate can provide indirect indicators of fluid and electrolyte balance.
Interpreting laboratory tests and physical exam findings is crucial for accurate assessment. For example, a low serum sodium level may indicate hyponatremia, while a high serum potassium level may indicate hyperkalemia.
Guidelines for monitoring fluid and electrolyte balance include:
- Regular monitoring of vital signs and weight
- Assessment of hydration status through physical exam
- Laboratory testing as indicated by clinical presentation
Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances
Fluid and electrolyte imbalances can occur due to various factors, including dehydration, excessive fluid loss, or electrolyte disturbances. The different types of fluid and electrolyte imbalances include:
- Dehydration:Loss of body fluids, leading to decreased intracellular and extracellular fluid volume
- Hypervolemia:Excess body fluids, leading to increased intracellular and extracellular fluid volume
- Hyponatremia:Low serum sodium levels, often due to excessive fluid intake or sodium loss
- Hypernatremia:High serum sodium levels, often due to dehydration or excessive sodium intake
- Hypokalemia:Low serum potassium levels, often due to excessive potassium loss or inadequate intake
- Hyperkalemia:High serum potassium levels, often due to decreased potassium excretion or excessive intake
Each imbalance has specific causes, symptoms, and consequences. For example, dehydration can cause fatigue, dizziness, and decreased urine output, while hyponatremia can lead to seizures, confusion, and coma.
Management of Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances
Management of fluid and electrolyte imbalances involves correcting the underlying cause and replacing lost fluids and electrolytes. Principles of management include:
- Assessment and monitoring:Accurately assessing the type and severity of the imbalance is crucial.
- Fluid replacement:Intravenous or oral fluids may be administered to correct dehydration or hypovolemia.
- Electrolyte replacement:Electrolytes may be administered intravenously or orally to correct electrolyte imbalances.
- Underlying cause management:Treating the underlying cause of the imbalance, such as diarrhea or vomiting, is essential.
The types of fluids and electrolytes used for replacement therapy depend on the specific imbalance. For example, isotonic fluids are used to correct dehydration, while hypotonic fluids may be used to correct hypernatremia.
Monitoring and adjustment of fluid and electrolyte replacement is essential to ensure effective management. Laboratory tests and clinical assessment are used to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments.
Interactive Exercises and Simulations: Interactive Tutorial Fluids And Electrolytes
Interactive exercises and simulations can enhance the learning experience by providing opportunities for learners to apply their knowledge and practice fluid and electrolyte management.
- Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Simulation:This simulation allows learners to manage fluid and electrolyte balance in a virtual patient, making decisions about fluid and electrolyte replacement.
- Case Study Analysis:Learners can analyze real-world case studies involving fluid and electrolyte imbalances, discussing the causes, symptoms, and management strategies.
- Quizzes and Games:Interactive quizzes and games can test learners’ knowledge of fluid and electrolytes in a fun and engaging way.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Case studies and real-world examples illustrate the application of fluid and electrolyte management in clinical practice.
- Case Study:A patient with severe diarrhea presents with dehydration and hyponatremia. Learners can discuss the management of this patient, including fluid and electrolyte replacement strategies.
- Real-World Application:A discussion of the challenges and decision-making involved in managing fluid and electrolyte imbalances in critically ill patients.
- Reflection:Opportunities for learners to reflect on their understanding and apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios.
Evaluation and Feedback
Evaluating the effectiveness of the interactive tutorial is crucial for improving the learning experience. Methods of evaluation include:
- Learner feedback:Collecting feedback from learners through surveys or questionnaires to assess their satisfaction, understanding, and suggestions for improvement.
- Knowledge assessment:Conducting pre- and post-tutorial assessments to measure learners’ knowledge gain.
- Observing learner engagement:Monitoring learner participation in interactive exercises and simulations to assess their engagement and understanding.
Feedback is used to improve the tutorial by addressing areas for improvement, updating content, and enhancing the overall learning experience.
General Inquiries
What is the purpose of an interactive tutorial on fluids and electrolytes?
An interactive tutorial on fluids and electrolytes aims to provide an engaging and interactive learning experience, allowing learners to actively participate in the learning process. It utilizes various interactive elements such as simulations, exercises, and case studies to enhance understanding and retention.
What are the benefits of using an interactive approach to teaching fluids and electrolytes?
An interactive approach offers numerous benefits, including improved engagement, increased knowledge retention, enhanced critical thinking skills, and better preparation for real-world clinical practice.
What types of interactive exercises and simulations are included in this tutorial?
This tutorial incorporates a range of interactive exercises and simulations, such as case studies, scenario-based challenges, and virtual patient simulations. These exercises are designed to provide learners with hands-on experience in assessing, diagnosing, and managing fluid and electrolyte disorders.
How is the effectiveness of this interactive tutorial evaluated?
The effectiveness of this interactive tutorial is evaluated through various methods, including learner feedback, knowledge assessments, and tracking of learning outcomes. Feedback from learners is collected through surveys and discussion forums, while knowledge assessments are conducted through quizzes and case study analysis.