Which coenzyme is the electron acceptor in the following reaction? This intriguing question unveils the fascinating realm of coenzymes and their pivotal role in cellular processes. As we delve into the intricate dance of electron transfer, we uncover the significance of these molecular helpers in driving the energetic machinery of life.
Coenzymes, the indispensable partners of enzymes, orchestrate a symphony of chemical reactions that sustain life. They act as electron carriers, facilitating the transfer of electrons between molecules, a process essential for energy production and countless metabolic pathways.
Coenzyme Definition
Coenzymes are organic molecules that participate in enzyme-catalyzed reactions as cofactors, facilitating chemical transformations without being permanently altered. They act as electron carriers, transferring electrons between substrates, and are essential for many biochemical reactions.
Electron Acceptor Function

In redox reactions, electron acceptors are molecules that receive electrons from electron donors. They play a crucial role in cellular metabolism, providing an electron sink for various metabolic processes, including respiration and photosynthesis.
Coenzyme Identification
Numerous coenzymes are involved in biological reactions, including:
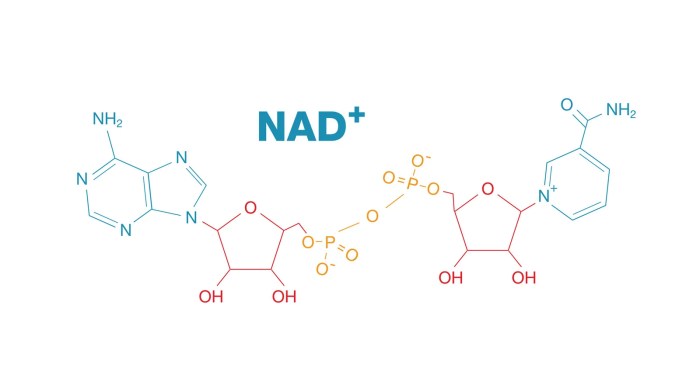
- Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD +/NADH)
- Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD/FADH 2)
- Coenzyme A (CoA)
- Ubiquinone (CoQ)
In the specified reaction, the coenzyme that acts as the electron acceptor is NAD +.
Electron Transfer Mechanism

NAD +accepts electrons from a substrate through a hydride ion transfer, becoming NADH. This process involves the transfer of two electrons and a proton. The chemical change is as follows:NAD ++ 2H ++ 2e –→ NADH + H +
Coenzymes and Metabolism: Which Coenzyme Is The Electron Acceptor In The Following Reaction

Coenzymes are essential in various metabolic pathways, including glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. NAD +, for example, plays a crucial role in glycolysis, where it accepts electrons from glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, facilitating the conversion of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
Essential FAQs
What is the primary function of coenzymes?
Coenzymes serve as electron carriers, facilitating the transfer of electrons between molecules in enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
Why are electron acceptors crucial in cellular metabolism?
Electron acceptors are essential for the efficient transfer of electrons during metabolic processes, allowing cells to generate energy and carry out vital functions.