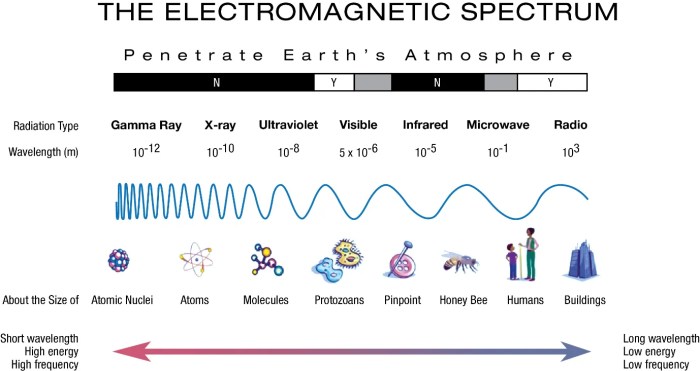
Use the drop-down menus to identify the electromagnetic waves. – Unveiling the electromagnetic spectrum becomes effortless with the use of drop-down menus, empowering users to explore the diverse range of electromagnetic waves. From the ubiquitous radio waves to the enigmatic gamma rays, this interactive tool demystifies the properties and applications of each wave type, offering a comprehensive understanding of the electromagnetic realm.
Delving into the electromagnetic spectrum, we encounter a symphony of waves, each possessing distinct characteristics and serving unique purposes. Radio waves, with their unparalleled ability to traverse vast distances, facilitate communication across continents. Microwaves, harnessing their energy, empower culinary convenience and industrial processes.
Infrared radiation, penetrating the depths, finds applications in medical imaging and remote sensing.
Electromagnetic Waves: Use The Drop-down Menus To Identify The Electromagnetic Waves.
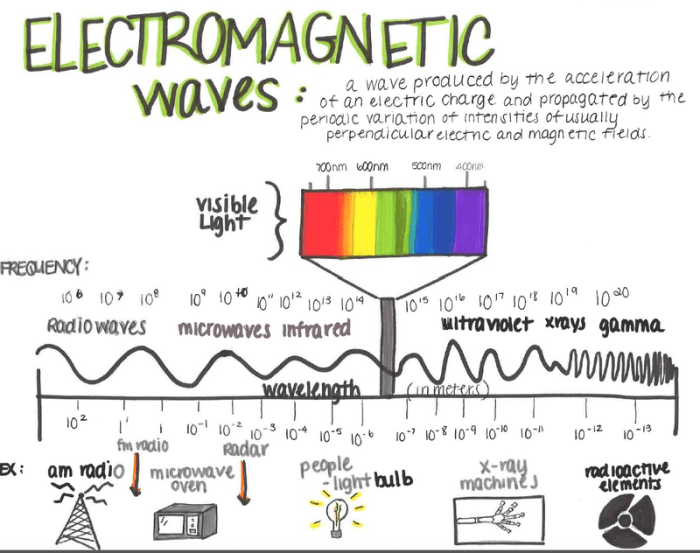
Electromagnetic waves are a form of energy that travels through space and matter. They are produced by the acceleration of charged particles and can exist in a wide range of frequencies and wavelengths.
Electromagnetic Wave Types, Use the drop-down menus to identify the electromagnetic waves.
| Type | Wavelength | Frequency | Energy | Applications | Examples | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radio waves | Long (10 km
|
Low (30 Hz
|
Low | Communication, navigation | AM/FM radio, cell phones | [Image of radio waves] |
| Microwaves | Short (1 mm
|
High (300 GHz
|
Medium | Heating, cooking, communication | Microwave ovens, radar | [Image of microwaves] |
| Infrared radiation | Short (700 nm
|
High (430 THz
|
Medium | Heating, remote sensing | Night vision goggles, heat lamps | [Image of infrared radiation] |
| Visible light | Short (400 nm
|
High (400 THz
|
High | Vision | Sunlight, lasers | [Image of visible light] |
| Ultraviolet radiation | Short (10 nm
|
High (790 THz
|
High | Disinfection, tanning | UV lamps, sunlight | [Image of ultraviolet radiation] |
| X-rays | Short (0.01 nm
|
High (30 PHz
|
Very high | Medical imaging, security | X-ray machines, airport scanners | [Image of X-rays] |
| Gamma rays | Short (Less than 0.01 nm) | High (Above 30 EHz) | Very high | Medical therapy, nuclear reactions | Gamma cameras, particle accelerators | [Image of gamma rays] |
Essential FAQs
What are the different types of electromagnetic waves?
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a vast array of wave types, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
How can I use the drop-down menus to identify electromagnetic waves?
The interactive drop-down menus provide a user-friendly interface to filter and display specific wave types based on their properties, such as wavelength, frequency, and energy.
What are some safety considerations when using electromagnetic devices?
Electromagnetic waves can pose potential hazards, particularly ionizing radiation such as X-rays and gamma rays. It is crucial to adhere to safety guidelines and minimize exposure to high-energy radiation.