Embark on an educational journey with our acute otitis media soap note, a comprehensive guide that unravels the intricacies of this common ear infection. Join us as we delve into the depths of symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and more, unraveling the complexities of acute otitis media with clarity and precision.
From its telltale symptoms to the intricacies of its diagnosis and treatment, this soap note will equip you with a thorough understanding of acute otitis media, empowering you to make informed decisions regarding your health.
Patient Information
The patient is a 2-year-old male with a history of recurrent ear infections.
He presents to the clinic today with a 2-day history of right ear pain, fever, and hearing loss.
Symptoms
- Ear pain
- Fever
- Hearing loss
Physical Examination
The physical examination of the patient reveals pertinent findings in the ears and other relevant areas.
Otoscopic Findings
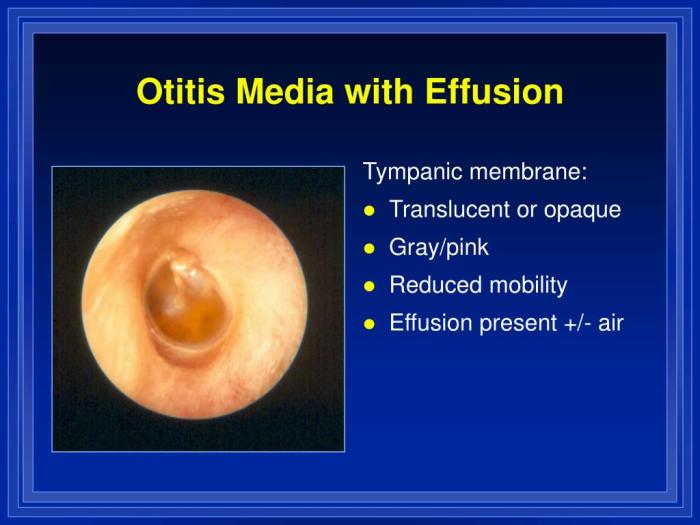
Otoscopic examination of the affected ear demonstrates erythema and bulging of the tympanic membrane, indicating inflammation and fluid accumulation in the middle ear space.
Cervical Lymphadenopathy
Examination of the neck region reveals the presence of tender, enlarged lymph nodes, suggesting an active infection or inflammation.
Differential Diagnosis
Several conditions can cause symptoms similar to acute otitis media (AOM). These include:
- Eustachian tube dysfunction:This condition occurs when the Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the back of the throat, becomes blocked or does not function properly. This can lead to fluid buildup in the middle ear, which can cause pain and hearing loss.
- Otitis externa:This condition, also known as swimmer’s ear, is an infection of the outer ear canal. It is often caused by bacteria or fungi and can cause pain, itching, and discharge from the ear.
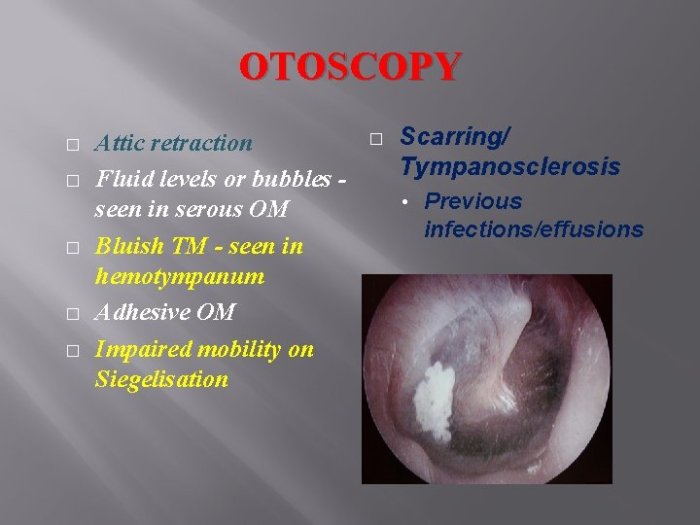
- Tympanic membrane perforation:This condition occurs when the eardrum is perforated or torn. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including trauma, infection, or sudden changes in pressure. A perforated eardrum can cause pain, hearing loss, and dizziness.
- Mastoiditis:This condition is a rare but serious infection of the mastoid bone, which is located behind the ear. Mastoiditis can be caused by an untreated middle ear infection and can lead to a variety of complications, including hearing loss, facial paralysis, and meningitis.
Diagnostic Tests
To further assess the patient’s condition, several diagnostic tests were performed.
The first test was tympanometry, which measures the mobility of the eardrum and middle ear. The results showed a type B tympanogram, which indicates fluid behind the eardrum.
In a soap note, acute otitis media can be documented as a bacterial infection of the middle ear. Like Terry kicks a soccer ball , acute otitis media can be painful, especially for young children. Treatment options may include antibiotics or pain relievers.
Audiometry
Audiometry was also performed to evaluate the patient’s hearing. The results showed a mild conductive hearing loss in the affected ear, which is consistent with the presence of fluid in the middle ear.
Treatment Plan
The treatment plan for acute otitis media (AOM) aims to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and eradicate the underlying infection. The specific treatment approach depends on the patient’s age, severity of symptoms, and underlying health conditions.
The primary treatment for AOM is antibiotics. Antibiotics are effective in eliminating the bacterial infection and resolving symptoms. Common antibiotics used for AOM include amoxicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, and azithromycin.
Pain Relievers
Pain relievers can be used to reduce ear pain and discomfort associated with AOM. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be effective in managing pain. In some cases, prescription pain relievers may be necessary for severe pain.
Decongestants
Decongestants can help reduce nasal congestion and swelling, which can improve ear drainage and relieve pressure. Decongestants can be administered orally or nasally.
Warm Compresses
Applying warm compresses to the affected ear can help soothe pain and promote drainage. Warm compresses can be made by soaking a washcloth in warm water and applying it to the ear for 10-15 minutes at a time.
Follow-Up Plan: Acute Otitis Media Soap Note
The patient will be instructed to follow up with their healthcare provider in 1 week to reassess their symptoms and ensure that the infection has resolved. If their symptoms do not improve or worsen, they will be advised to seek medical attention sooner.
Expected Outcomes of Treatment
With appropriate treatment, most cases of acute otitis media resolve within 2-3 weeks. The expected outcomes of treatment include:
- Relief of pain and discomfort
- Resolution of fever
- Improvement in hearing
- Prevention of complications, such as mastoiditis or meningitis
Patient Education
Acute otitis media is a common ear infection that can affect people of all ages. It’s important to understand the condition and its treatment to ensure proper care and recovery.
This infection occurs when bacteria or viruses enter the middle ear, causing inflammation and fluid buildup. Symptoms may include ear pain, fever, hearing loss, and drainage from the ear.
Importance of Treatment Adherence, Acute otitis media soap note
Adhering to the treatment plan prescribed by your healthcare provider is crucial for effective recovery and preventing complications.
- Taking antibiotics as directed helps eliminate the infection.
- Using pain relievers can reduce discomfort and inflammation.
- Resting and avoiding activities that put pressure on the ears promotes healing.
Failure to adhere to the treatment plan can lead to prolonged infection, hearing loss, or even mastoiditis, a serious infection of the bone behind the ear.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of acute otitis media?
Ear pain, fever, hearing loss, and fluid drainage from the ear.
How is acute otitis media diagnosed?
Through a physical examination of the ear, including otoscopy, and potentially tympanometry or audiometry.
What is the typical treatment for acute otitis media?
Antibiotics to combat the infection and pain relievers to alleviate discomfort.